Progress report on rustc_codegen_cranelift (November 2024)
There has been a fair bit of progress since the last progress report! There have been 383 commits since the last progress report.
You can find a precompiled version of cg_clif at https://github.com/bjorn3/rustc_codegen_cranelift/releases/tag/dev or in the rustc-codegen-cranelift-preview rustup component if you want to try it out.
Achievements in the past eight months
ABI
There have been significant improvements in the ABI compatibility between the Cranelift and LLVM backends. Most of these improvements affect the Rust ABI across all targets, but some only affect a single platform. In the latter case I will mention them under the section of the respective target. One of the improvements is a partial fix to the Rust ABI where rustc depended on LLVM inventing a calling convention when more values are returned than fit in the registers reserved for returning values by the native calling convention. It is hard for the Cranelift backend to match whatever calling convention was invented by LLVM. For the GCC backend, it is likely impossible to match the convention.
- #1523: Update abi-cafe
- issue wasmtime#9250: Cranelift: Incorrect abi for i128, i128 return value on x86_64 sysv
- issue wasmtime#9509: Cranelift: Correctly handle abi calculation for multi-part arguments
- rust#131211: Return values larger than 2 registers using a return area pointer
- rust#132729: Make fn_abi_sanity_check a bit stricter
- wasmtime#8875: Various cleanups to the ABI handling code
- wasmtime#8903: Various cleanups to the ABI handling code (part 1)
- wasmtime#9253: Couple of cleanups to the ABI computation
- wasmtime#9258: Remove StructArgument support from the arm64, riscv64 and s390x backends
- wasmtime#9267: Couple of improvements to the abi handling code (part 3)
- wasmtime#9284: Couple of improvements to the abi handling code (part 4)
- wasmtime#9287: Make the Tail call conv follow the system call conv for the return area ptr
- issue wasmtime#9510: Cranelift: Remove support for implicitly adding a return area pointer
- wasmtime#9511: Gate support for implicit return area pointers behind an option
Windows
raw-dylib support for Windows has been implemented by @dpaoliello and @ChrisDenton. This was the last blocker before distributing cg_clif as rustup component for Windows. Thanks a lot to both for all the work!
- issue #1345: Implement raw-dylib for Windows
- ar_archive_writer#15: Add the ability to create PE import libraries (thanks @dpaoliello!)
- ar_archive_writer#17: Add support for creating archives with members from an import library (thanks @dpaoliello!)
- ar_archive_writer#23: Make the null import descriptor name unique to the import library (thanks @ChrisDenton!)
- rust#128206: Make create_dll_import_lib easier to implement
- rust#129164: Use ar_archive_writer for writing COFF import libs on all backends (thanks @ChrisDenton!)
- 322c2f6: Sync ar_archive_writer to LLVM 18.1.3
- #1524: Add support for raw-dylib (thanks @dpaoliello!)
- rust#128939: Distribute rustc_codegen_cranelift for Windows
- #1537: Don’t panic about debug info for Arm64 Windows unwind info (thanks @dpaoliello!)
macOS
Support for calling variadic functions has long been a blocker for arm64 macOS support. While Rust doesn’t support defining variadic functions, it does need to be able to call several variadic functions like ioctl. As Cranelift doesn’t have native variadic function support, I have been hacking in support in cg_clif by taking advantage of the fact that in most calling conventions variadic arguments are passed the exact same way as regular arguments, so I could cast the defined function signature of the callee to one which lists all variadic arguments as regular arguments. On arm64 Apple however decided to force all variadic arguments to be passed on the stack1. As a concequence of this, the hack cg_clif used doesn’t work. A couple months back first contributor @beetrees opened a PR which adds another hack on top of the existing hack to add enough dummy arguments to force the actual variadic arguments to be passed on the stack as they should be. In the future I would like to add native support for variadic functions to Cranelift, but until then this hack unblocked support for arm64 macOS. It is now available as rustup component too.
- #1515: enable abi-cafe tests on aarch64-apple-darwin (thanks @lqd!)
- #1500: Fix varargs support on aarch64-apple-darwin (thanks @beetrees!)
- rust#127177: Distribute rustc_codegen_cranelift for arm64 macOS
- object#702: Reverse the order of emitting relocations on MachO
- 253436c: Better parsing of
#[section_name]on Mach-O - f340c81: Statically enable a couple of target features always enabled on arm64 macOS
Performance
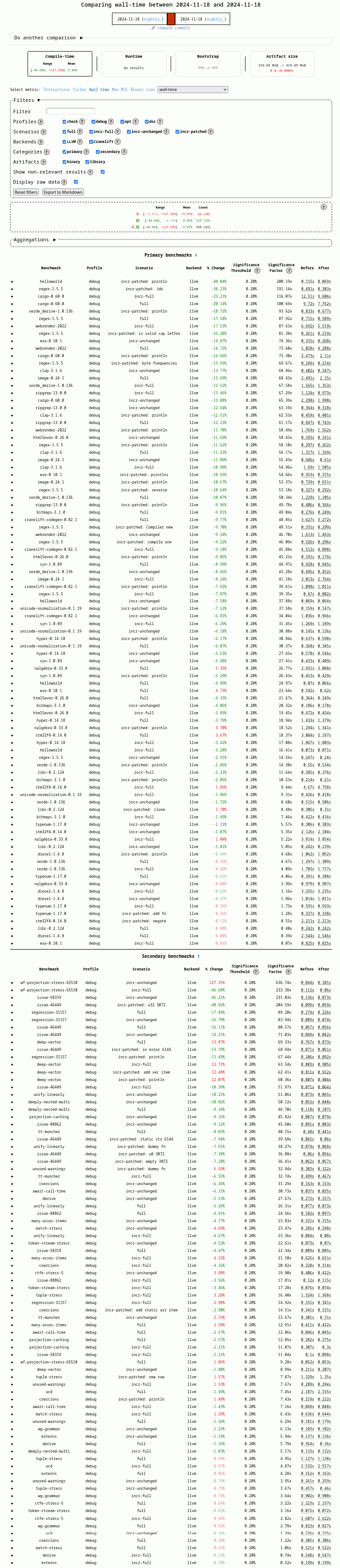
I recently ran the rustc-perf benchmark suite on cg_clif first the first time in a very long time. The results were pretty bad with many benchmarks showing significant regressions compared to cg_llvm. After comparing profiler output between cg_clif and cg_llvm, it became quite clear why the regressions happened: When nightly rustc switched to using lld by default on Linux, this was only done when using the LLVM backend. The reason for this was that Cranelift didn’t yet use TLSDESC on arm64 and lld only supports the TLSDESC thread local storage implementation. This was fixed later, but rustc was never changed to allow lld with cg_clif until I opened a PR a couple of days ago. The next nightly showed much better benchmark results with most benchmarks being 10-50% faster. A couple of secondary benchmarks still showed some non-trivial regressions, but all of them are pathological code. Still I did look further into the coercions benchmark. This showed significantly more time spent writing the object file than compiling to clif ir. Turns out I forgot to wrap the File to which the object file is written in a BufWriter, so it did a ton of tiny writes. Adding the BufWriter completely fixed the regressions on this benchmark.
Moral of the story: Benchmark more often.
In any case some work is being done on making it easier to do local benchmarks and in the future getting https://perf.rust-lang.org to routinely benchmark cg_clif and compare it against cg_llvm.
One of the GSoC projects was adding a faster register allocator to Cranelift. This was successfully done and @d-sonuga (who worked on this) has shown quite promising benchmark results on their blog. Cranelift only started to support selecting this new register allocator a couple of days ago, and it hasn’t made it to a stable release of Cranelift yet. Because of this I haven’t benchmarked it myself yet.
Benchmark results. (warning: very long images)
Left: before these changes. Right: after these changes.
- #1489: Translate MIR to clif ir in parallel with parallel rustc
- #1541: Use a BufWriter in emit_module to reduce syscall overhead
- #1542: Disable clif ir verifier by default
- rust#132774: Use lld with non-LLVM backends
- wasmtime#7201: aarch64: Implement TLSDESC for TLS GD accesses (thanks @afonso360!)
- https://d-sonuga.netlify.app/gsoc/regalloc-iii/
- wasmtime#9611: Cranelift: add option to use new single-pass register allocator.
Inline assembly
A couple of improvements to inline assembly support this time.
- #1481: Allow MaybeUninit in input and output of inline assembly (thanks @taiki-e!)
- cba05a7: Support naked functions
SIMD
A whole bunch of new vendor intrinsics were implemented by contributors.
- #1488: add the llvm.x86.sse42.crc32.32.32 intrinsic (thanks @folkertdev!)
- #1490: add all llvm.x86.sse42.crc32.. intrinsics (thanks @folkertdev!)
- #1491: add llvm.x86.avx2.permd intrinsic (thanks @folkertdev!)
- 8f1d41e: Implement _rdtsc x86 vendor intrinsic
- #1495: add llvm.x86.sse2.cvtps2dq (thanks @folkertdev!)
- c48b010: Implement x86 _mm_sqrt_ss vendor intrinsic
- #1533: aarch64 neon intrinsics: vmaxq_f32, vminq_f32, vaddvq_f32, vrndnq_f32 (thanks @tjamaan)
Challenges
SIMD
While core::simd is fully supported through emulation using scalar operations, many platform specific vendor intrinsics in core::arch are not supported. This has been improving though with the most important x86_64 and arm64 vendor intrinsics implemented.
If your program uses any unsupported vendor intrinsics you will get a compile time warning and if it actually gets reached, the program will abort with an error message indicating which intrinsic is unimplemented. Please open an issue if this happens.
- issue #171: std::arch SIMD intrinsics
Cleanup during stack unwinding on panics
Cranelift currently doesn’t have support for cleanup during stack unwinding. I’m working on implementing this and integrating it with cg_clif.
Until this is fixed panic::catch_unwind() will not work and panicking in a single thread will abort the entire process just like panic=abort would. This also means you will have to use -Zpanic-abort-tests in combination with setting panic = "abort" if you want a test failure to not bring down the entire test harness.
- issue wasmtime#1677: Support cleanup during unwinding
ABI
There are still several remaining ABI compatibility issues with LLVM. On arm64 Linux there is a minor incompatibility with the C ABI, but the Rust ABI works just fine. On arm64 macOS there are several ABI incompatibilities that affect the Rust ABI too, so mixing cg_clif and cg_llvm there isn’t recommended yet. And on x86_64 Windows there is also an incompatibility around return values involving i128. I’m slowly working on fixing these.
- issue #1525: Tracking issue for abi-cafe failures
Contributing
Contributions are always appreciated. Feel free to take a look at good first issues and ping me (@bjorn3) for help on either the relevant github issue or preferably on the rust lang zulip if you get stuck.
-
https://developer.apple.com/documentation/xcode/writing-arm64-code-for-apple-platforms#Update-code-that-passes-arguments-to-variadic-functions ↩